Introduction and Overview
This Portfolio is a documentation of the contributions that I have made during the development of the application, titled NUSSU Connect.
NUSSU Connect is a CLI application developed by team F09-1 and it aims to cater to the needs of executive committee members of the NUS Student Union (NUSSU).
It comes with multiple features that NUSSU executive committee members will find useful. This includes budgets and expenses management, human resource allocation, easy management of contacts lists, and all the information stored within this application will have an additional security guarantee by the multi-user access level feature.
Summary of contributions
In this project, my main contribution is in the Search Pruning feature and the main purpose of this feature is to ease the process of managing a large list of contacts. Further details about my contributions will be explained in this section.
-
Major enhancement: Search Pruning feature with
findandundofindcommands.-
What it does: Each subsequent execution of
findcommands allows users to search according to the current displayed list of contacts.undofindcommand does the opposite and reverts the lastfindcommand executed. -
Why we need this feature: NUSSU exco is an organization that will most likely be required to keep track of a large database of important contacts. Therefore it will be time-consuming and tedious to locate specific contact information from the database. A search pruning feature will resolve this problem as users will be able to narrow down the search space in discrete steps so that they could retrieve the information they want in smaller and readable chunks.
-
Highlights: This enhancement is mainly created from scratch with some help from documentations on how the
Predicateclass works. This enhancement was also created with re-usability in mind and any form of filtering done withPredicatewill be able to utilize this feature.
-
-
Minor enhancement: Added an enhancement to Search Pruning Feature that allows users to see a history of keywords that they have executed previously.
-
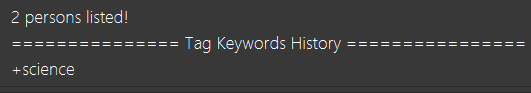
What it does: Every time a user performs a search, the command result box will display the list of keywords previously executed by the user and it describes how the current displayed list is being filtered.
-
-
Minor enhancement: Improved find command by introducing searching by tags and exclude functionality.
-
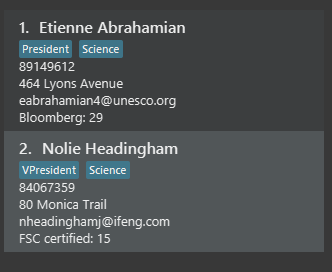
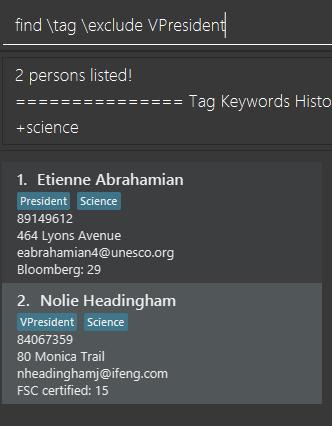
What it does: Searching by tags allows users to filter the contacts according to the tagged description of each contact. Exclude functionality allows users to remove unwanted results from their search.
-
-
Code contributed: [Overview]
-
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Managed releases
v1.1,v1.2,v1.2.1andv1.3(4 releases) on GitHub. -
Managed milestones and deadlines of the project.
-
-
Documentatations:
-
Updating Class Diagrams of Model in developer guide to reflect the changes in implementation. (Pull Requests #144).
-
Minor Tweaks to ReadMe, User Guide and Developer Guide to meet module requirements.
-
-
Tools:
-
Setting up of Coveralls in team repository
-
-
Community:
-
Contributions to the User Guide
This section shows part of my contributions in the User Guide that explains to end-users about how they can utilize the Search Pruning Feature. |
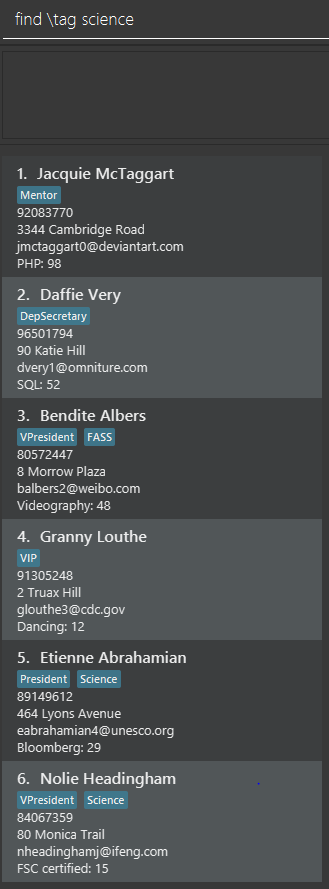
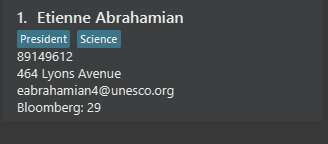
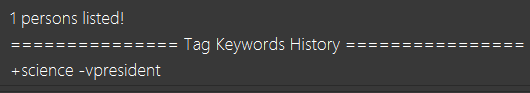
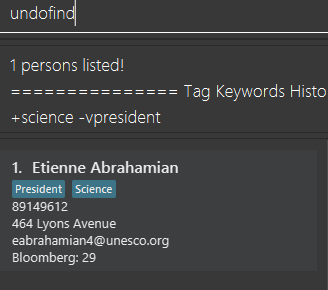
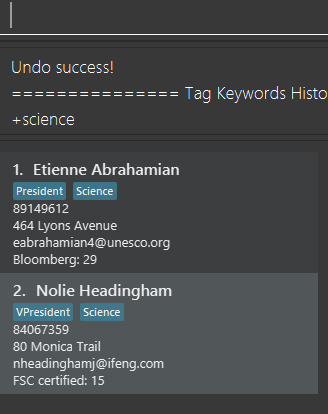
Search Pruning Feature with list, find and undofind commands
The Search Pruning feature was introduced to NUSSU Connect in v1.1 and it lets you trim the list of contacts with every successive find command. This feature will you to search through a large list of contacts in a much more intuitive manner without the hassle of typing a long single line command that is usually error-prone.
To provide you with an idea on how you can utilize the Search Pruning feature, the concept of the Search Pruning
feature will be further illustrated with the example below
1. Search Pruning with Find Commands
2 . Making a mistake and undoing it with undofind command
Contributions to the Developer Guide
This section shows part of my contributions in the Developer Guide that explains the underlying implementation behind the Search Pruning feature. |
Search Pruning Feature
The Search Pruning mechanism is facilitated by the SearchHistoryManager class, and within it is a searchHistoryStack that stores Predicate objects.
Predicate objects are used to filter FilteredList objects by calling the setPredicate() method of FilteredList. By storing Predicate objects
in SearchHistoryManager, it stores the search logic that was previously used by the FilteredList object, and hence, simulates the storing Search History
without storing the actual data.
In NUSSU Connect, the main SearchHistoryManger object is in ModelManager and it stores Predicate<Person> objects used for the filtering of filteredPersons list.
If you want to utilize SearchHistoryManager for your own use case, you can initialize a new SearchHistoryManager object with its' generic constructor.
|
Current Implementation
The main implementation behind SearchHistoryManager is a Stack Data Structure and the following 4 methods of SearchHistoryManager are exposed for your usage
-
executeNewSearch(Predicate<T> predicate)
updates system search logic to the next state and returns aPredicateobject storing the system search logic after the update. -
revertLastSearch()
reverts system search logic to the previous state and returns aPredicateobject storing the system search logic after revert. -
clearSearchHistory()
clears all system search logic from in-app memory. -
isEmpty()
returns true ifsearchHistoryStackis empty.
Given below are illustrations to help you understand how the first three method works internally. But before carrying on, you need to take note of the following.
| In the diagrams, 'UP' is the short-form for User Predicate and 'SP' is the short-form for System Predicate. User Predicate stores the logic specified by the user and it is not the actual search logic used for filtering of FilteredList objects. On the other hand, System Predicate stores the search logic for the system and it will be used to filter FilteredList objects. |
| User Predicate and System Predicate are not actual Classes and they are simply there to help simplify the explanation. In the actual implementation, there is no way to differentiate one from the other. |
executeNewSearch(Predicate<T> predicate)
Upon calling this method, there will be two different situations
-
Situation 1:
searchHistoryStackis empty
Upon receiving a new User Predicate, SearchHistoryManager will simply push the new User Predicate intosearchHistoryStackas a System Predicate.
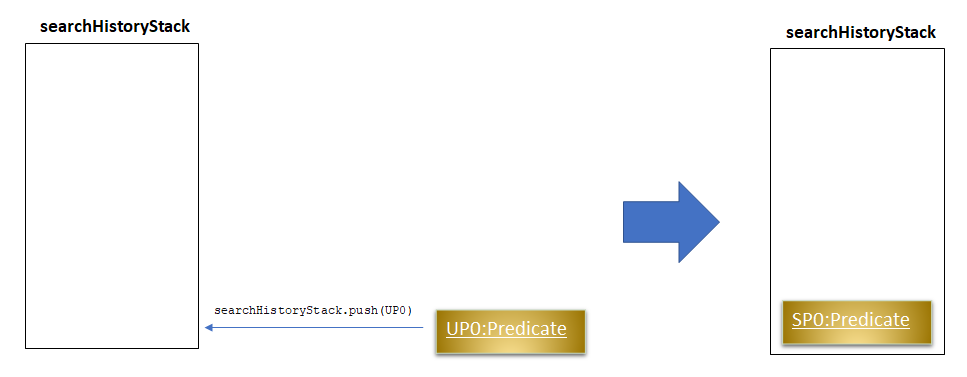
-
Situation 2:
searchHistoryStackis not empty
Before pushing the newPredicateinto the stack,SearchHistoryManagerwill first retrieve the System Predicate object at the top of the stack. After retrieving it, it will call theand()method with the User Predicate, creating a new System Predicate which will then be pushed into the top of the stack.
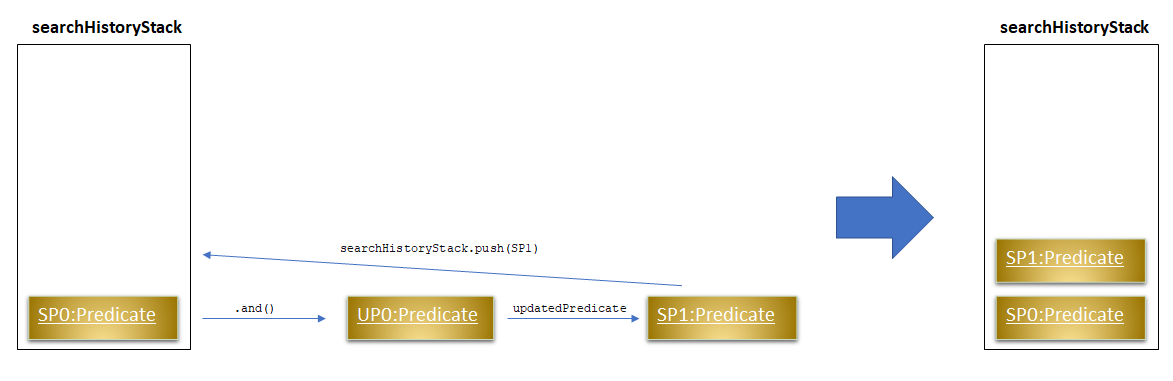
This method will return the new System Predicate at the top of the stack.
revertLastSearch()
This method will pop the System Predicate at the top of the stack.
In the event that the stack is already empty, this method will throw EmptyHistoryException.
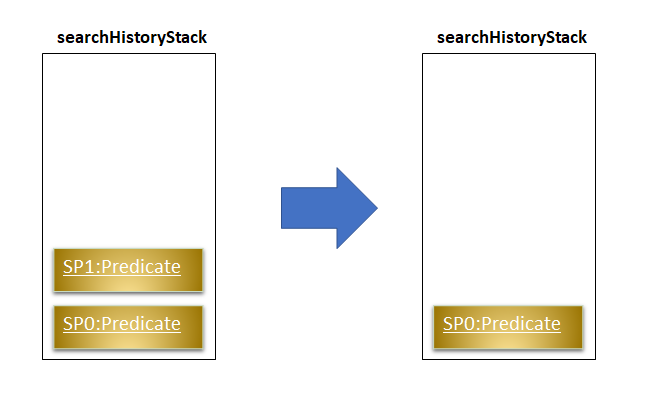
If the stack is not empty after the pop, this method will return the System Predicate at the top of the stack. Else,
it will return a Predicate object with a search logic that always defaults to true.
clearSearchHistory()
This method will simply empty the stack.
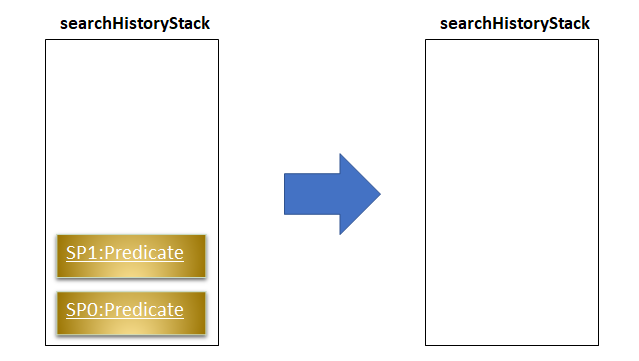
How SearchHistory
The following sequence diagrams shows you how the IncludeNameFindCommand and UndoFind commands
utilize SearchHistoryManager to perform Search Pruning. Other variations of FindCommand works similarly to
IncludeNameFindCommand and the sequence diagram for IncludeNameFindCommand is also relevant to them.
-
IncludeNameFindcommand
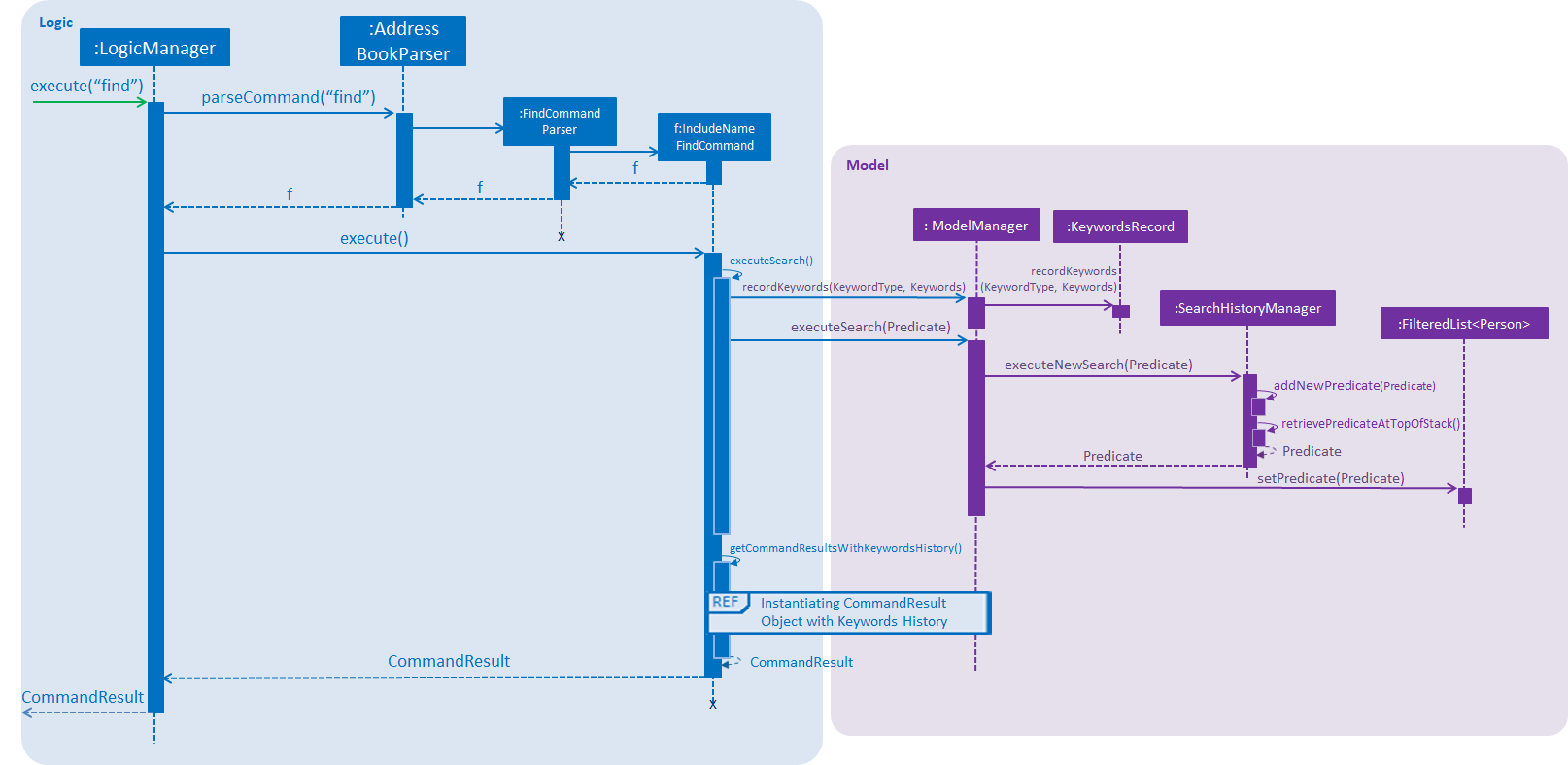
-
UndoFindcommand
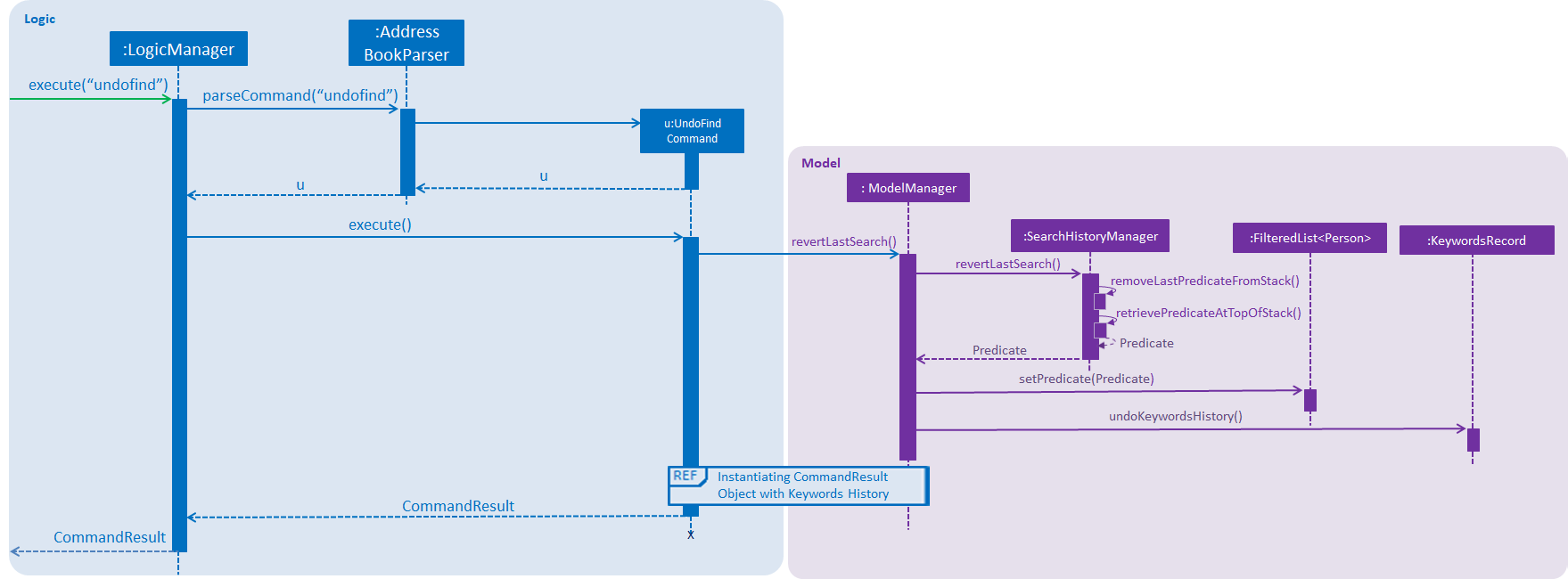
Design Considerations
Aspect: What data is stored in search history stack
-
Alternative 1(current choice): Save a Stack of
Predicateobjects-
Pros:
-
Does not need to store the data in search history explicitly which saves memory
-
SearchHistoryManagerclass is reusable for any Search Pruning done withPredicate
-
-
Cons:
-
Developers need to understand how
Predicateworks before utilizingSearchHistoryManagerto perform Search Pruning. -
Predicateobjects by itself does not perform the Search Pruning. We have to make an additional call to thesetPredicate()method of theFilteredListclass with thePredicateobject.
-
-
-
Alternative 2: Save a Stack of Lists containing
Personobjects in search history-
Pros:
-
It is easy to understand from the code that we are filtering according to
Personobjects.
-
-
Cons:
-
More memory is required as
Personobjects has to be duplicated multiple times into a new Lists. -
SearchHistoryManagercan only be used for Search Pruning on objects that is aPerson.
-
-
Aspect: How the Predicate at the top of the Stack is retrieved from SearchHistoryManager
-
Alternative 1(current choice):
Predicateis returned from the methodsexecuteSearch()andrevertLastSearch()-
Pros:
-
No need for an extra method call to retrieve system search logic in the form of
PredicatefromSearchHistoryManager.
-
-
Cons:
-
No clear distinction between Update and Retrieval of system search logic.
-
-
-
Alternative 2:
Predicateis not returned from the methodsexecuteSearch()andrevertLastSearch(), but is instead retrieved with another method.-
Pros:
-
Clearer distinction between Update and Retrieval of system search logic.
-
-
Cons:
-
Need to perform 2 method calls separately to retrieve
Predicateobject fromSearchHistoryManagerafter an update to search logic. -
Need to implement another method specifically for retrieval of
Predicateobject. -
Other developers utilizing
SearchHistoryMangerneed to remember that they need to retrievePredicateobject fromSearchHistoryManagerseparately after an update to search logic.
-
-